Under Attack: How 2FA Prompt Bombing Targets Human Weakness
2FA Prompt Bombing is a type of cyberattack where an attacker floods a user with repeated two-factor authentication (2FA) push notifications in an attempt to wear them down. The goal is to trick the user into approving one of the requests out of frustration or confusion, granting the attacker access. It exploits the human factor in 2FA systems rather than technical vulnerabilities.
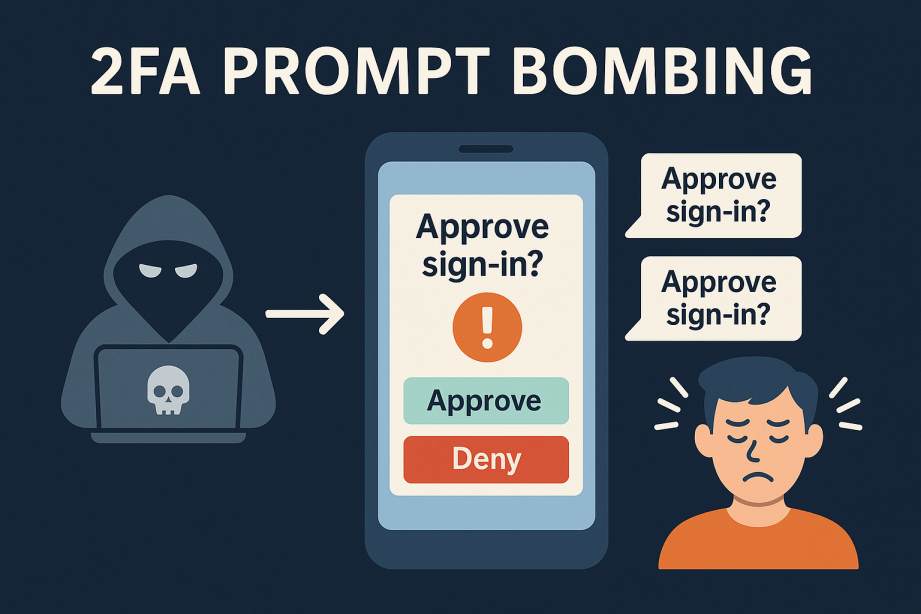
What Is 2FA Prompt Bombing?
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) is a critical security measure designed to add an extra layer of protection to user accounts. It typically requires users to provide something they know (like a password) and something they have (such as a mobile device for a verification code). While 2FA significantly enhances security, attackers have begun exploiting a weakness in the way it's implemented through a tactic known as 2FA prompt bombing.
2FA prompt bombing, also called MFA fatigue or push bombing, is a social engineering attack where a malicious actor floods a victim's device with repeated 2FA push notifications. The goal is to annoy, confuse, or wear down the target until they eventually approve one of the prompts, inadvertently giving the attacker access to their account.
How Does It Work?
Here’s a typical scenario:
- An attacker obtains a victim’s login credentials through phishing, data leaks, or brute force.
- The attacker attempts to log into the victim’s account, triggering a 2FA push notification (e.g., through an app like Duo, Okta Verify, or Microsoft Authenticator).
- The attacker sends dozens or even hundreds of these prompts in a short period.
- The victim, overwhelmed or annoyed, might mistakenly or out of frustration approve the request.
- The attacker gains access and bypasses the intended security of 2FA.
In some cases, attackers may contact the victim (pretending to be IT support) to convince them to accept the prompt under false pretenses—blending technical exploitation with psychological manipulation.
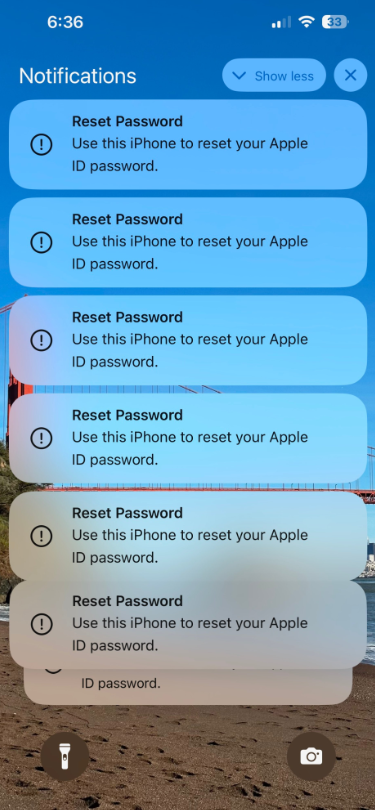
Example of 2FA Prompt bombing, where attackers try to gain access to Apple ID:
Why this attack is significantly dangerous?
2FA prompt bombing highlights a critical issue in security: user behavior is often the weakest link.
1. Exploits Human Error
Security systems are often designed with technical defenses, but prompt bombing targets human psychology. Repeated notifications can cause users to act without thinking, especially if they’re distracted, busy, or confused.
2. Bypasses a Trusted Security Layer
2FA is widely regarded as a best practice for securing accounts. If users can be tricked into approving malicious requests, it undermines the effectiveness of one of our most trusted security tools.
3. Difficult to Detect
Unlike brute-force attacks or malware, prompt bombing doesn’t rely on code or exploit technical vulnerabilities. It's subtle and hard for automated systems to distinguish from legitimate user behavior—making detection and prevention trickier.
4. Gaining Popularity Among Attackers
This method has been used in high-profile breaches, including attacks on major corporations and government organizations. Its simplicity and effectiveness make it appealing to cybercriminals.
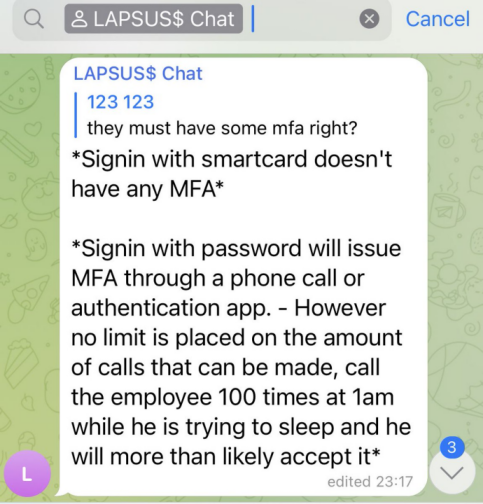
The infamous cybercrime group "LAPSUS$" admits to using 2FA prompt bombing on their Telegram channel:
How to Protect Against 2FA Prompt Bombing
Organizations and users can take several steps to mitigate this threat:
-
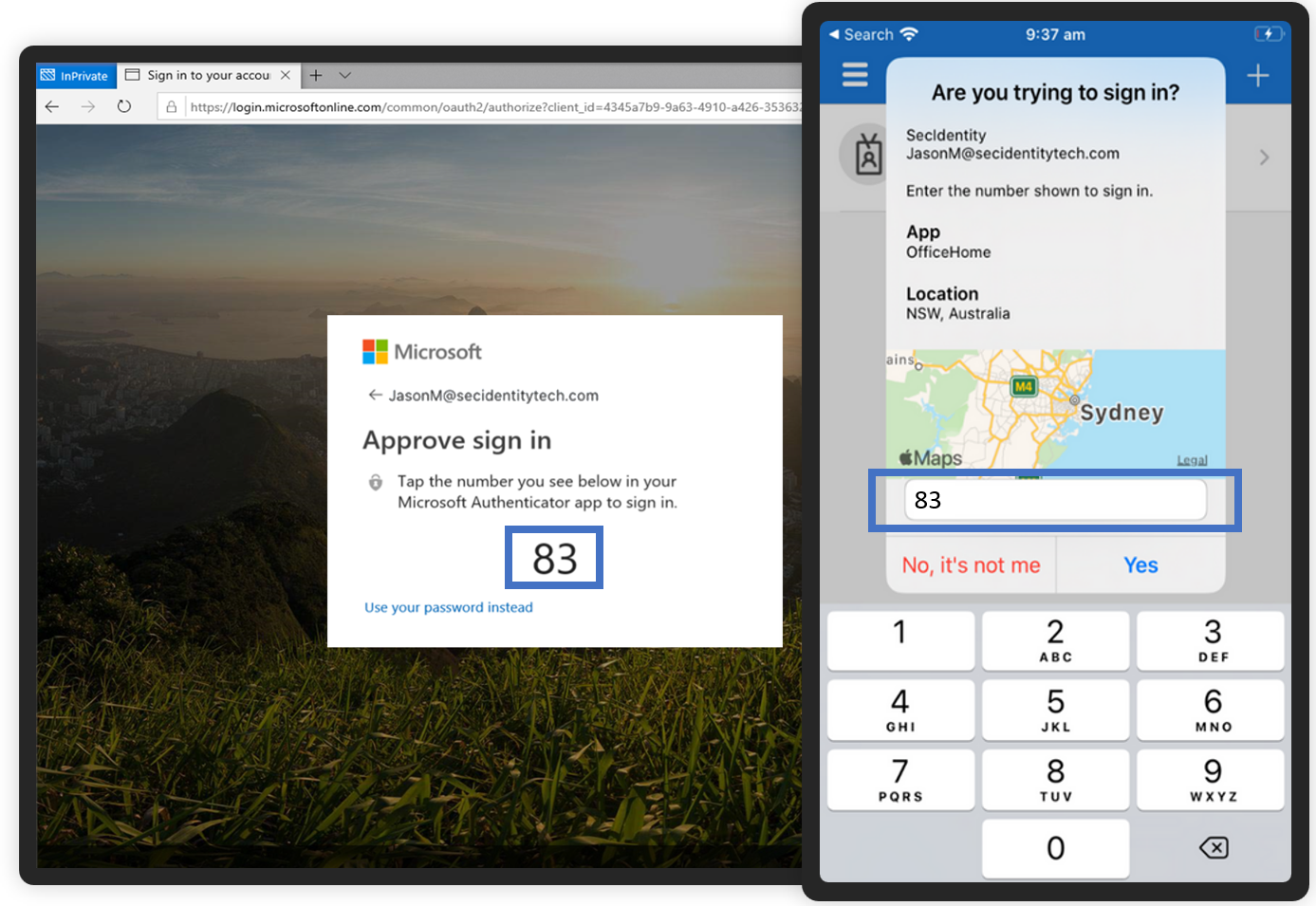
Use Number Matching or Verification Codes: Instead of simple
approve/denyprompts, some apps now require the user to enter a code or match a number shown on the login screen—making accidental approvals less likely.A demonstration of the "Number matching" technique when logging in to a Microsoft account using Authenticator:
-
Limit Retry Attempts: Systems can restrict how many times a user is prompted within a certain period, helping to prevent floods of requests.
-
Educate Users: Awareness is crucial. Users should know not to approve unexpected prompts and to report any suspicious activity.
-
Adopt Phishing-Resistant MFA: Solutions like security keys (e.g., YubiKey) or biometric verification offer more robust protection against social engineering.
Social engineering is a manipulation technique used to trick people into giving away confidential information or performing actions that compromise security. Instead of attacking systems directly, it targets human psychology—such as trust, fear, or urgency.
-
Monitor and Alert: Implement logging and alerts for repeated MFA prompt requests, which can signal an attempted attack.
Final Safety Recommendations
-
How to easily and effectively increase cybersecurity in your company? Check out how Redamp.io can help protect you.
-
Stay informed! Read our blog and follow notifications in the app about the latest threats we are monitoring for you.
-
Be cautious! Pay special attention to phishing and ransomware .
Sources: krebsonsecurity.com , beyondtrust.com , jeffreyappel.nl , techcommunity.microsoft.com